Mauritania Country Report
Mauritania, located in Northwest Africa, is characterized by its vast desert landscapes, diverse ethnic groups, and Islamic heritage. The country has a rich history, with ancient trading routes crossing its territory. Since gaining independence from France in 1960, Mauritania has faced challenges related to political instability, ethnic tensions, and economic development. The government operates within a framework of Islamic law, with a mix of traditional and modern institutions shaping governance. Mauritania’s economy relies heavily on agriculture, mining, and fishing, with significant income disparities between urban and rural areas. The country also grapples with issues such as poverty, unemployment, and human rights concerns. Despite these challenges, Mauritania has made progress in recent years, particularly in areas such as education and healthcare. Efforts to diversify the economy, improve infrastructure, and address social inequalities remain ongoing priorities for the government and international partners.
Last updated: April 11, 2022
Security
Mauritania faces various security challenges, both domestic and regional. Domestically, the country contends with threats from terrorism, particularly from groups affiliated with Al-Qaeda and ISIS operating in the Sahel region. These groups have targeted security forces, government officials, and civilians, posing a significant security risk. Additionally, Mauritania grapples with issues such as organized crime, including drug trafficking and human smuggling, which thrive in the vast desert landscapes and porous borders.
Regionally, Mauritania is affected by instability in neighboring countries, such as Mali and Libya, which have experienced conflict and political upheaval. The spillover effects from these conflicts, including the proliferation of arms and the movement of extremist groups, further complicate Mauritania’s security landscape.
To address these challenges, Mauritania has strengthened its security forces and cooperates with regional and international partners, including the United Nations and the African Union, to combat terrorism and address security threats in the Sahel region. However, addressing the root causes of insecurity, such as poverty, marginalization, and governance issues, remains crucial for achieving lasting peace and stability in Mauritania.
Last updated: April 29, 2022
Infrastructure
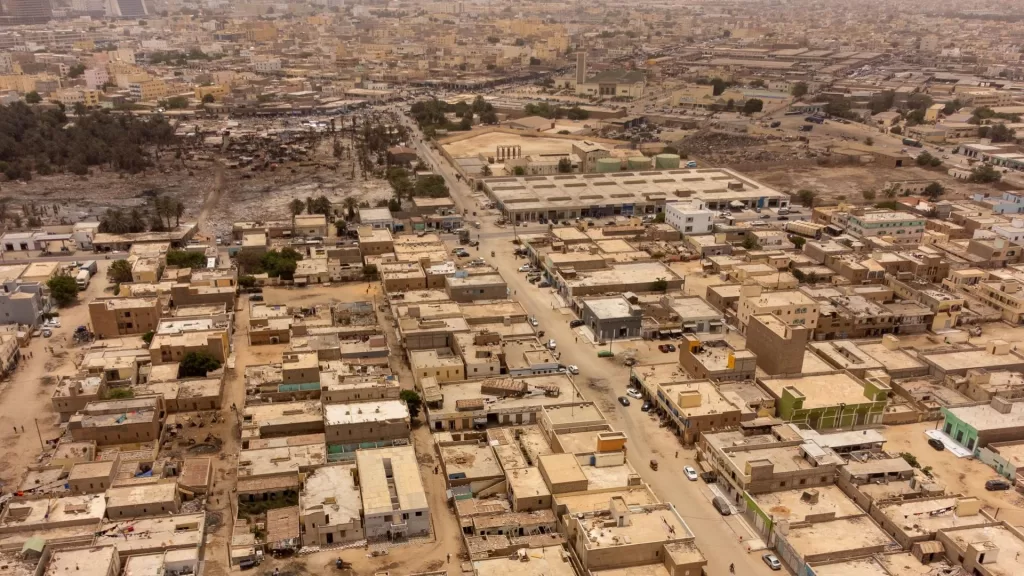

Mauritania’s infrastructure is characterized by significant challenges, particularly in transportation and utilities. The country’s vast desert terrain poses difficulties for road construction and maintenance, resulting in limited road networks, particularly in rural areas. Many roads are unpaved and poorly maintained, which hinders transportation and economic development. Additionally, Mauritania’s railway system, primarily used for transporting iron ore from mines in the interior to the coast, requires modernization to improve efficiency and safety.
Access to electricity and clean water is also limited, particularly in rural and remote areas. While urban centers like Nouakchott have relatively better infrastructure, many rural communities lack access to reliable electricity and safe drinking water. Furthermore, sanitation infrastructure is inadequate, contributing to health and environmental concerns.
To address these challenges, Mauritania has embarked on infrastructure development projects with support from international partners. These initiatives aim to improve road networks, expand access to electricity and water, and modernize transportation systems. However, more investments and concerted efforts are needed to address Mauritania’s infrastructure deficiencies and promote sustainable development across the country.
Last updated: April 29, 2022
Environment
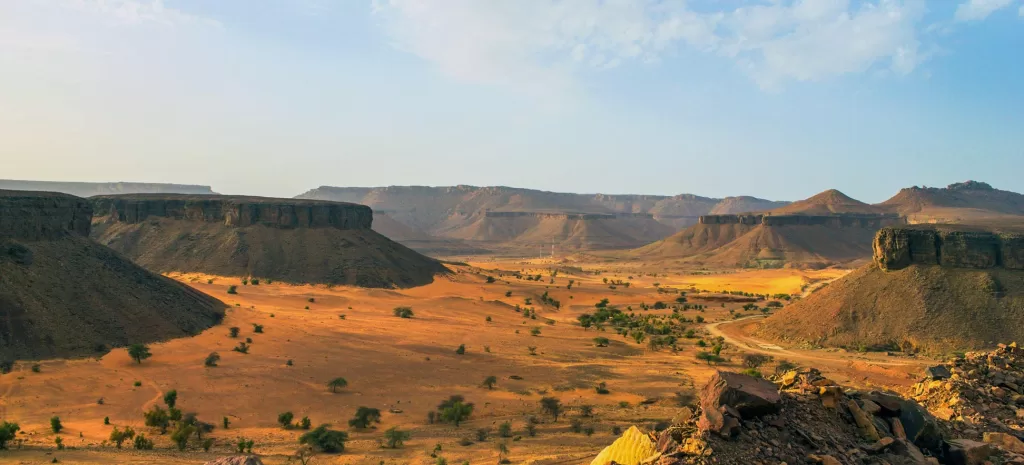

Mauritania’s environment faces various challenges, including desertification, water scarcity, and deforestation. The country’s largely arid and semi-arid climate makes it vulnerable to desertification, exacerbated by factors such as overgrazing, unsustainable agricultural practices, and climate change. Desertification threatens agricultural productivity, natural habitats, and livelihoods, particularly in rural areas where many communities rely on farming and pastoralism for their survival.
Water scarcity is also a significant environmental issue in Mauritania, with limited access to freshwater sources, particularly in the interior regions. This scarcity is compounded by over-extraction, inefficient irrigation practices, and competing demands from agriculture, industry, and domestic use.
Furthermore, deforestation and habitat degradation pose threats to Mauritania’s biodiversity and ecosystems. Forests, particularly in the southern regions, are being cleared for agriculture, urbanization, and fuelwood, leading to loss of biodiversity and disruption of ecosystems.
To address these environmental challenges, Mauritania has implemented various initiatives, including reforestation projects, sustainable land management practices, and water conservation measures. International partnerships and support from organizations such as the United Nations and the African Union also play a role in addressing environmental issues and promoting sustainable development in Mauritania. However, concerted efforts are needed to mitigate the impacts of desertification, water scarcity, and deforestation and ensure the long-term environmental sustainability of the country.
Last updated: March 15, 2022
Health and Medical
Mauritania’s healthcare system faces challenges in providing adequate services, particularly in rural and remote areas, where access to healthcare facilities and trained medical professionals is limited. The country grapples with high rates of infectious diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis, and cholera, exacerbated by factors including poor sanitation, limited access to clean water, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure. Additionally, malnutrition and maternal and child health remain significant concerns, contributing to high mortality rates among infants and pregnant women. Efforts to improve healthcare delivery, strengthen primary care services, and address public health challenges are ongoing, with support from international organizations and donor countries. However, sustained investment and collaboration are needed to address the root causes of health disparities and improve healthcare outcomes for all Mauritanians.
Last updated: March 31, 2022
Political
Mauritania’s political situation is characterized by a delicate balance between democratic governance and authoritarian rule. Despite transitioning to multiparty democracy in 2006, the country has experienced frequent military coups and government changes throughout its history. President Mohamed Ould Ghazouani, who assumed office in 2019 after winning a controversial election, faces criticism for alleged human rights abuses and crackdowns on political opposition. Additionally, Mauritania’s political landscape is influenced by ethnic and tribal dynamics, with power often concentrated among the Arab-Berber elite. The government’s control over media and civil society organizations further restricts political freedoms, although there have been efforts to improve transparency and accountability in recent years. As Mauritania navigates the complexities of political reform and societal change, tensions between authoritarian governance and democratic aspirations continue to shape the country’s political trajectory.
Last updated: March 25, 2022















